Deep neural networks
Deep learning is a technique that is part of the broader family of machine learning methods. Together these techniques form an ever more important part of the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The most crucial feature making these techniques so succesfull and broadly applicable is that they can learn from data. More traditional AI techniques required users to handcraft features that they would like to recognize in their data, taking a lot of time and expertise, while leading to suboptimal algorithms. With machine learning and deep learning such data features are learned automatically, saving time and leading to insights that might not be expected beforehand.
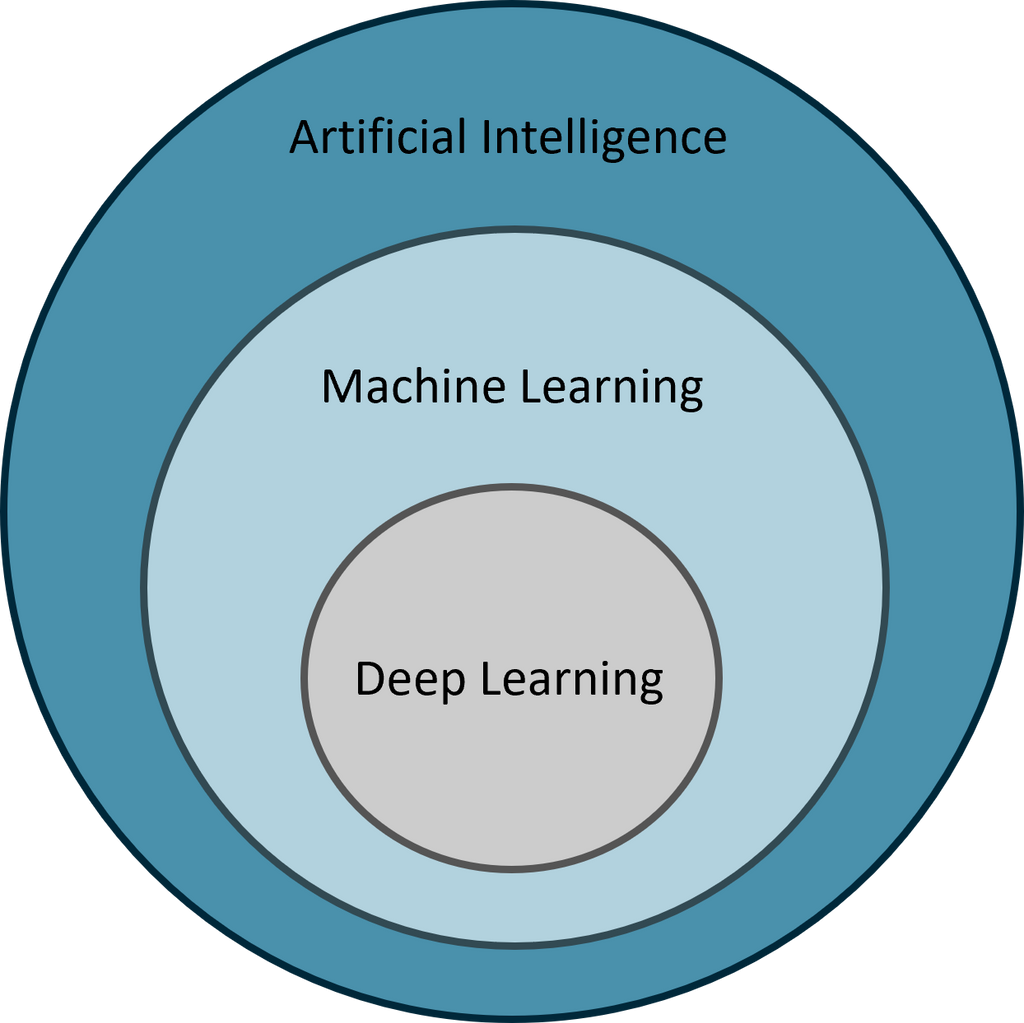
Deep learning distinguishes itself from machine learning by using 'deep' algorithm architectures, which means that the information processed by a deep learning algorithm goes through multiple computational 'layers'. The more of these 'layers', the deeper an algorithm is. The processing of information by deep learning algorithms is often compared to how our brain works. Deep learning algorithms have a similar architecture to our brain, in the sense that information is processed by individual units called 'neurons', which are connected to many other 'neurons'. The connection strengths between all these 'neurons' determines the functioning of the whole algorithm, just like how the connections in our brain determine how we observe the world.
Deep learning is thus a technique that is highly successful in learning from large amounts of structured data. The fact that deep learning algorithms automatically learn data features is its most important aspect, but can also pose a challenge in interpreting the output of a deep learning algorithm. Such algorithms are often considered a 'black box' since we do not know exactly based on what data features the algorithm makes a decision. There are, however, more and more ways to gain insight in the inner workings of such algorithms, for example through visualisation of the data features or through the creation of heatmaps that show what part of the data an algorithm bases its decision on. Such insights are crucial for the responsible usage of deep learning algorithms, for example by preventing unethical biases in algorithms.
Applications of deep learning
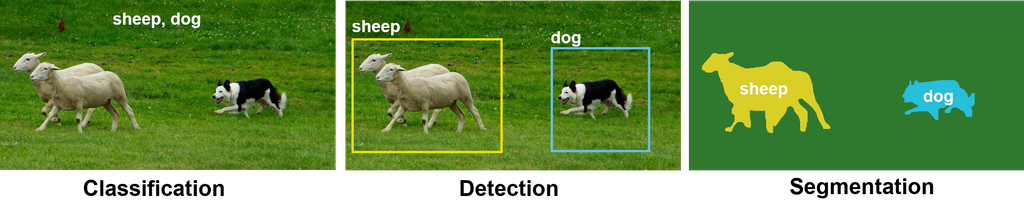
Deep learning has initially been very successfull in interpreting image data, but has by now become the most important tool for the interpretation of text, audio, video, time signals, genetics and many more types of data. The types of tasks deep learning algorithms that can perform on these data types is very extensive. Some of the more common tasks on image data include: classification of images, like recognizing if a disease is present or not, segmentation of images for example in different anatomical parts or object detection, like the detection of lesions.